Search Engine Marketing : Introduction
1. What is search engine marketing?
Search Engine Marketing concept was evolved in 90’s.
SEM should be done properly and regularly to attract huge traffic towards website.
Search Engine Marketing is the method used to get visibility on a search engine result page with the aim to drive qualified traffic to a site. SEM is based on PPC model (Pay Per Click). Here advertiser or user only pays the search engine when a click has been made on the ad.
Search Engine Marketing is used for promoting ones business, website with the help of organic methods or non-organic methods (Ex: PPC) or both. By doing this it can help in increasing of ranking of your website in the search engine result page.
2. What are the major search marketing platforms?
Google (Google Adwords)
Microsoft (Bing)
Yahoo
3. Why is Search Engine Marketing Important?
SEM can help in brand awareness
SEM can help companies/individuals to sell their products, services or content online.
SEM can be used to generate online leads and increase sales
When using internet we find pop-ups that are used as ads. User may be interested in ad and click on it and this create chance of getting lead.
Search Engine helps in personalizing ads which are providing non-intrusive and non-distraction ads which are helpful and provide relevant information
Paid Search:
Google / Facebook constantly runs auctions to determine who is the current highest-bidder for paid search ads.
Much like “PageRank” for organic search results, sponsored links are ordered according to their : AdRank=Maximum CPC x Quantity Score
The “Quality Score” for a sponsored link depends on
- How closely the ad seller’s keywords match the user’s search keywords.
- How good the page is that the sponsored link points to
- The prior CTR(Click-Through-Rate) performance of that sponsored link
What is Page Rank?
Page Rank is name of the Algorithm in Google that helps in displaying your results against search queries.
How does AdRank work?
AdRank is determined on the relevance of Search Query, Keywords, Quality, Content, Prior CTR Performance.
If a page has ranked once but later due to keyword stuffing or other way. If rank goes down. He will never ranked high again to that level. Because to the page to which the sponsored Ad is pointing to does not have appropriate content.
Prior CTR performance of the sponsored Ad, Relevance and content is Important for getting good AdRank. If you have sponsored link which has very low CTR will suppress the entire SEM efforts.
What can Google do for Advertisers?
Google can help Advertiser to meet many objectives by helping to track, determine and measure metrics to succeed in their campaign.
Google can help is Generate Awareness to Targeted Impressions
Build Brand to bring Qualified visits to your website or page
Educate prospects by providing in depth involvement
Generate leads and request for proposal
Identify prospects and allow them to download Coupons, Register for Newsletter, Register for E-Mail Address opt-ins
Benefits of Adwords : Reach
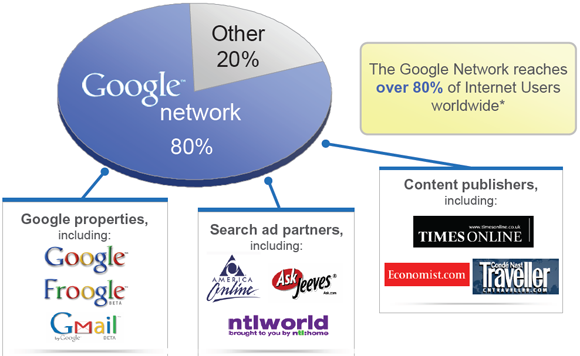
Source : https://neilpatel.com/blog/8-techniques-thatll-double-your-google-adwords-conversion-rate/

Source : https://www.slideshare.net/rahulkavaiya07/rahulkavaiya-online-advertising
Google’s Advertising platform is also called as Adwords
Microsoft’s Advertising platform is also called as Bing
Growth in Search:

Source : http://slideplayer.com/slide/7486431/
Search-based advertising will be one-third of all online ad spending by 2008
Direct Marketing and offline Media Growth is slowing
Marketers are choosing search Advertising Instead of other media.
Search Now the Largest Share of Online Ads.
% of Online Advertising Revenue.

Source : http://slideplayer.com/slide/3827774/
Metrics :
Cost Per Lead, often abbreviated as CPL, is an Online advertising pricing model, where the advertiser pays for an explicit sign-up from a consumer interested in the advertiser’s offer.
Cost Per Lead = Cost of Generating Leads/Total Leads Acquired
Consider your company spent $500 on your pay-per-click (PPC) campaign and 10users convert to leads
Cost per lead = $500/10 = $50
Cost Per Acquisition : Cost Per Acquisition(CPA) measures how much it costs in advertising to convert one person from a visitor to a client for the company
Source : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cost_per_lead
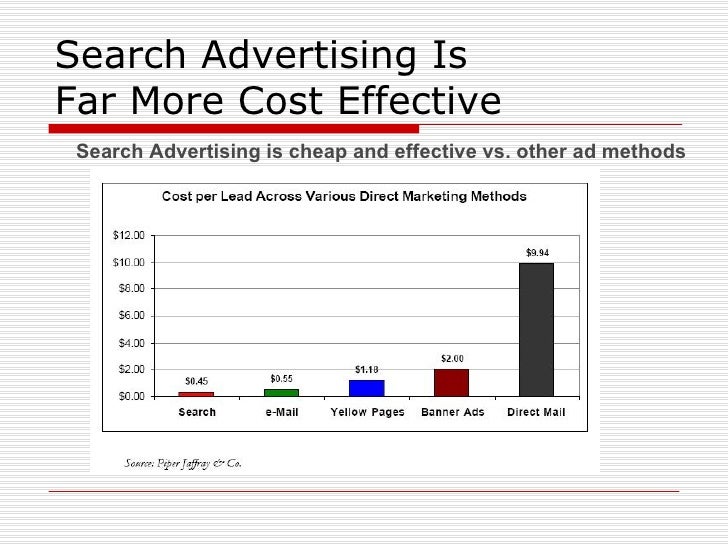
Source : https://www.slideshare.net/nishagarg21/brief-on-pay-per-click-ppc-for-beginners
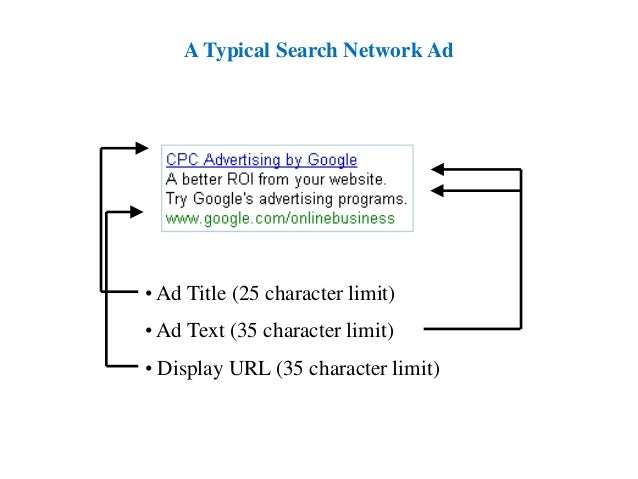
Source : https://www.slideshare.net/Manish4u786/google-adword-29216397
Why should you use PPC?
- People who search Google are actively looking for related information ie. in most cases they are in ‘buy mode’ the opposite to social media
- Real-time adjustments to campaigns and bids-pause campaigns if you have site issues and stay in complete control of you budgets.
- Option of using Google Content (Display) Network with further option for using Google’s ‘Remarketing’ scheme.
- Demographic and Geographic targeting
- Approximately two out of three clicks on the first page are from PPC Adverts.
- Adjustments of campaigns for effective ROI and within CPA limits (expertise required)
When should you use PPC
When to use Adwords
- Competive or Unique Product
- Special Event
- New Product

Source : http://alpssolutions.com/google-adwords.php
Budget (How cost effective is PPC)
- Largely dependent on sector and campaigns
- Keywords (groups) should be analysed for most effective CPA (Sweet-spot). There is a point where increasing the CPC bids will have little effect on conversions.
Definitions:
- Sponsored Search :
- Pay-Per-Click distribution tactic that displays your ads in the sponsored search results at the top, along the side and across the bottom of search results page for searches that relate to your keywords
- Content Placement Targeting:
- Pay-Per-Click distribution tactic that displays your ads alongside relevant articles such as product reviews, news articles etc on the Yahoo and Google distribution network
- Ad Text :
- The marketing message displayed to prospective customers. An Ad contains a title, discription and URL
- Landing Page :
- The Page on a website where one is taken after clicking on a advertisement. While this can be any page, it is often a page designed to expand on the service or product mentioned in the initial advertisement.
- Campaign:
- A campaign contains one or more ad groups sharing the same budget, schedule and Geo-targeting criteria. A campaign is typically created to support a particular marketing goal.
- Keyword:
- A word or phrase that relates to the products or services you wish to advertise when prospective customers are looking for information related to what you sell and they type your targets into a search box, your ads may be displayed.
- Conversions:
- The completion of an action that you value, such as a purchase, registration, or sign-up
- Impressions:
- The number of times an ad is displayed in search results or on sites.
- Click-Through-Rate(CTR):
- The number of clicks received divided by the number of impressions generated.
- Example : An Ad that is displayed 100 times & receives 10 clicks has a Click-Through-Rate of 10%.
- AVE CPC:
- Average Cost Per Click. The average price you paid each time your was clicked.
Source : https://dfwsem.org/presentations/PPC_Back_to_Basics.ppt
Comments